题目描述
小萌非常喜欢能被 7 整除的数字,比如 7, 21, 121996,等等。
有一天她得到了 n 个正整数,她想用这些数制造出更多的能被
7 整除的数。于是她从这 n 个数中选出两个数,
然后将一个数写在另一个输的前面,一次得到一个新的数。
按这种方法她一共可以得到 $2\times \binom{n}{2}$ 个数。
她想知道在这些数中,有多少个是能被7整除的。
输入
第一行包含一个整数 n , $2 \le n \le 10^5$
第二行包含 n 个正整数 $a_i$ ,$1 \le a_i \le 10^9$
输出
输出一个整数
背景知识
群 (group)

域 (field)

有限域的例子
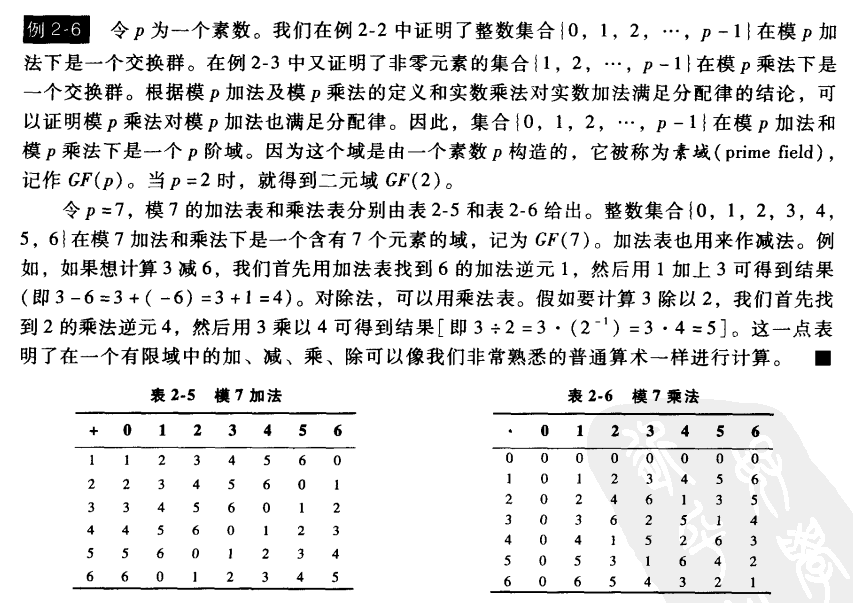
这个例子证明了对任意的素数 p ,存在一个含 p 个元素的有限域。
事实上,对任意正整数 m ,都可以吧一个素域 GF(p) 扩展成一个有
$p^m$ 个元素的域,称为 GF(p) 的扩域 (extension field),
记作 $GF(p^m)$ 。更进一步说,已经证明任何有限域的阶都是一个
素数的幂。为纪念它们的发现者,有限域也成为伽罗华域 (Galois field)。
由于域在加法运算下是封闭的;又因为域中元素的个数有限。
因此,必存在两个正整数 $m, n$ ,满足 $m < n$且
这个等式说明 $\sum_{i=1}^{n-m} 1 = 0$。
所以必然存在一个使得 $\sum_{i=1}^{\lambda} 1 = 0$
的最小正整数$\lambda$,这个整数 $\lambda$ 称为域
GF(q) 的特征值(characteristic),容易证明 $\lambda$
是一个素数。当 $q \ne \lambda$时,$q$ 是 $\lambda$的幂。
令$a$为GF(q)中的非零元素。
由于GF(q)中的非零元素在乘法下是封闭的,下列$a$的幂
必然也是GF(q)中的非零元素。由于GF(q)是有限域,
所给出的$a$的幂不可能各不相同。
也就是说,必然存在两个正整数 $k$ 和 $m$,使得 $m > k$
且$a^k=a^m$。令$a^{-1}$为$a$的乘法逆元,则
$\left(a^{-1}\right)^k=a^{-k}$是$a^k$的乘法逆元。
在$a^k=a^m$的两端同时乘以$a^{-k}$,得
这个等式说明必然存在一个使得$a^n=1$的最小正整数。
这个整数 $n$ 称为域元素 $a$ 的阶(order)。
定理 若 $a$ 为有限域 GF(q) 中的一个非零元素,则
$a^{q-1}=1$.
定理 若 $a$ 为有限域 GF(q) 中的一个非零元素,
n 为 a 的阶,则 n 必能整除 q - 1.
在有限域 GF(q) 中,如果 a 的阶为 q - 1,则非零元素
a 被称为本原元 (primitive element)。
因此,本原元的幂生成了 GF(q) 中的所有元素。
任何一个有限域都有一个本原元。

以上图片来自 差错控制编码 作者: [美] 林舒(Lin,S.) 第2章 代数引论 2.1 2.2
问题分析
两数组合能被7整除的充要条件
已知 A, B 为正整数,A 是 n 位数,若
$\overline{BA} = B \times 10^{n} + A \equiv 0\quad (mod\ 7)$,
则 B 需要满足什么约束?
注意到:
\(\begin{split}
10^n =& \left(3 + 7\right)^n = 3^n + \sum_{i = 1}^n C_n^i 3^{n-i}7^i\
\equiv & 3^n\quad (mod\ 7)
\end{split}\)
将条件两边同时模以 7,在GF(7)中运算,
$B’=\sum_{i=1}^B 1$ ,
$A’=\sum_{i=1}^A 1$ ,
有:
当 $7\ |\ A$时,问题是平凡的。此时,$7\ |\ B$。
因此,对于 A ,只需关注在 6 类不同的余数,以及 6 类不同的十进制位数(digit)下,
分别确定B的余数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int match[7][7] = {0};
int three[] = {1, 3, 2, 6, 4, 5};
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
match[i][j] = (7 - i) * three[(6 - j) % 6];
match[i][j] %= 7;
cout << match[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果如下:
6 2 3 1 5 4
5 4 6 2 3 1
4 6 2 3 1 5
3 1 5 4 6 2
2 3 1 5 4 6
1 5 4 6 2 3
计数方法
预处理输入数据,统计能被 7 整除的数的个数 cnt0,
统计输入不能被 7 整除时,按余数(i)及十进制位数(j)分类,
每种类型的输入个数cnt[i, j],再分别求出 6 种余数(不按十进制位数分类)的总数S[i]。
即为所求的结果。
实现
时间复杂度 o(n) (输入时间复杂度 o(n))
空间复杂度 o(1)
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
int n;
int an;
int count[7][7] = {0};
int &count0 = count[0][0];
int match[7][7] = {0};
int three[] = {1, 3, 2, 6, 4, 5};
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// if log10() is time consuming, read an as a string
// then get the length of string and convert it to integer.
cin >> an;
if (an % 7) {
count[an % 7][((int)ceil(log10(1 + an))) % 6]++;
} else {
count0++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
count[i][6] += count[i][j];
match[i][j] = (7 - i) * three[(6 - j) % 6];
match[i][j] %= 7;
}
}
unsigned long long total = count0 * (count0 - 1);
for (int i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
total += count[i][j] * count[match[i][j]][6];
}
}
cout << total << endl;
return 0;
}